Clean and safe water is the lifeblood of any thriving society, underpinning public health, supporting industrial processes, and sustaining delicate ecosystems. However, the natural water cycle often delivers raw water burdened with a myriad of impurities, ranging from dissolved minerals and organic matter to microscopic contaminants that can pose significant risks. Transforming this raw water into a potable and usable resource requires a complex and carefully orchestrated series of treatment processes. Among the diverse array of chemicals employed in this critical endeavor, soda ash, also known as sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), stands out as a versatile and indispensable workhorse. This seemingly simple white, odorless powder plays a pivotal role in addressing a spectrum of water quality challenges, contributing significantly to the effectiveness and efficiency of water treatment facilities worldwide.
For centuries, humans have sought ways to improve the quality of their water sources. While early methods relied on rudimentary techniques like boiling and filtration, the advent of modern chemistry brought forth sophisticated tools and compounds capable of tackling more complex contaminants. Soda ash, with its alkaline nature and unique chemical properties, emerged as a key ingredient in this evolution. Its ability to readily dissolve in water, yielding carbonate and bicarbonate ions, unlocks a cascade of beneficial reactions that target some of the most prevalent and problematic water quality issues. From neutralizing corrosive acidity and softening hard water to enhancing the removal of heavy metals and optimizing coagulation processes, the influence of soda ash permeates numerous stages of water treatment.
This article delves into the multifaceted applications of soda ash within the realm of water treatment. We will explore the fundamental chemical principles that underpin its effectiveness, unraveling the reactions that allow it to adjust pH, precipitate hardness-causing minerals, and facilitate the removal of undesirable contaminants. Furthermore, we will examine the specific stages of water treatment where soda ash plays a crucial role, highlighting its importance in both municipal drinking water production and the treatment of industrial wastewater. Understanding the advantages of utilizing soda ash, such as its cost-effectiveness, availability, and environmental profile when used responsibly, provides valuable insight into its continued prevalence in the industry. By exploring both the benefits and the essential considerations for its application, including proper dosage, safety protocols, and potential interactions with other treatment processes, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the power and versatility of soda ash as a cornerstone of modern water treatment practices. Ultimately, appreciating the role of this seemingly unassuming chemical underscores the intricate science behind the clean water we often take for granted.
- Understanding Water Treatment Challenges
- The Chemistry of Soda Ash in Water
- Key Applications of Soda Ash in Water Treatment
- Advantages of Using Soda Ash in Water Treatment
- Considerations and Best Practices for Using Soda Ash
- Question is how Soda Ash is made?
- Key Applications of Soda Ash Worldwide
- Uses and Benefits of Soda Ash in Water Treatment
- Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
- Soda Ash in Wastewater Treatment
- Safety and Handling of Soda Ash in Water Treatment
- Conclusion
Understanding Water Treatment Challenges
The journey from a raw water source to a supply of clean, safe water is fraught with challenges. Natural water bodies – whether rivers, lakes, or groundwater aquifers – are rarely pristine. They often carry a complex cocktail of dissolved and suspended substances, both naturally occurring and introduced through human activities. Understanding the nature and impact of these contaminants is fundamental to appreciating the necessity of water treatment and, consequently, the vital role played by chemicals like soda ash. Without effective intervention, these water quality issues can have severe consequences for human health, damage infrastructure, and disrupt ecological balance.
One of the most fundamental challenges in water treatment is managing acidity and low pH. Pure water has a neutral pH of 7.0. However, natural processes like the dissolution of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and the decomposition of organic matter can lower the pH, making the water more acidic. Furthermore, industrial discharges, acid rain resulting from atmospheric pollution, and the leaching of acidic compounds from soil and rocks can significantly exacerbate this issue. Acidic water is corrosive to pipes and infrastructure, leading to the leaching of heavy metals like lead and copper into the water supply, posing serious health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. Low pH can also disrupt aquatic ecosystems, harming fish and other aquatic life. In the context of treatment, acidic raw water requires neutralization to protect infrastructure and ensure the effectiveness of subsequent treatment processes. This is where the alkaline nature of soda ash becomes critically important, providing a safe and effective means of raising the pH to acceptable levels.
Another pervasive challenge is water hardness, primarily caused by the presence of dissolved divalent cations, predominantly calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions. These minerals are naturally present in many water sources due to the weathering of rocks like limestone and dolomite. While not a direct health hazard in moderate concentrations, hard water presents a multitude of practical problems. It reduces the effectiveness of soaps and detergents, leading to increased consumption and the formation of stubborn scum. In household appliances like washing machines, dishwashers, and water heaters, hard water leads to the formation of scale – a hard, crusty deposit of calcium and magnesium carbonates. This scale buildup reduces efficiency, increases energy consumption, shortens the lifespan of appliances, and can clog pipes and fixtures. Industrially, hard water can cause significant problems in boilers and cooling towers, leading to decreased heat transfer efficiency, increased maintenance costs, and potential equipment failure. Water softening is therefore a crucial aspect of water treatment in many regions, and soda ash, through its ability to precipitate calcium and magnesium carbonates, offers a valuable tool in achieving this.
Beyond pH and hardness, the presence of dissolved metals poses another significant challenge. Metals like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), arsenic (As), lead (Pb), and mercury (Hg) can occur naturally in groundwater or be introduced through industrial pollution and mining activities. Even in trace amounts, many heavy metals can be toxic to humans, causing a range of health problems, including neurological damage, kidney disease, and cancer. Removing these dissolved metals often requires specific treatment processes. While soda ash doesn’t directly react with all heavy metals, its ability to raise the pH can indirectly aid in their removal. Many metal ions become less soluble at higher pH levels, forming insoluble hydroxides or carbonates that can then be precipitated and filtered out of the water. This pH adjustment facilitated by soda ash can be a crucial step in a multi-stage treatment process for metal removal.
Furthermore, water sources can be contaminated with a variety of biological contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and algae. While soda ash itself is not a primary disinfectant, maintaining a proper pH balance, which soda ash helps achieve, can indirectly influence the effectiveness of disinfection processes like chlorination. For instance, chlorine is more effective as a disinfectant at slightly acidic to neutral pH levels. Additionally, excessive nutrient levels in water sources can lead to algal blooms, which can produce toxins, deplete oxygen levels, and impart unpleasant tastes and odors to the water. While soda ash doesn’t directly kill algae, managing the overall water chemistry, including pH and potentially influencing the availability of certain nutrients, can contribute to a healthier aquatic environment and reduce the likelihood of severe algal blooms.
Finally, the presence of suspended solids, such as silt, clay, and organic particles, contributes to turbidity, making the water cloudy and aesthetically unappealing. These suspended solids can also harbor microorganisms and interfere with disinfection processes. While soda ash is not directly involved in removing suspended solids, it plays an indirect role in the coagulation and flocculation processes that are essential for their removal. By adjusting the pH to an optimal range, soda ash can enhance the effectiveness of chemical coagulants like alum or ferric chloride. These coagulants neutralize the surface charge of the suspended particles, allowing them to clump together (coagulate) into larger, heavier flocs that can then be easily settled or filtered out.
In conclusion, the challenges faced in transforming raw water into a safe and usable resource are multifaceted and complex. Issues like acidity, hardness, dissolved metals, biological contaminants, and suspended solids all require targeted treatment strategies. Understanding the chemical properties and reactivity of treatment chemicals like soda ash is crucial in developing effective solutions to these challenges. The subsequent sections of this article will delve deeper into the specific ways in which soda ash addresses these water quality concerns, highlighting its indispensable role in the intricate science of water treatment.
The Chemistry of Soda Ash in Water
The effectiveness of soda ash in water treatment stems directly from its fundamental chemical properties and the reactions it undergoes when dissolved in water. Understanding these chemical mechanisms is key to appreciating its versatility in addressing various water quality challenges. At its core, soda ash, or sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), is an inorganic salt of carbonic acid and sodium. Its behavior in aqueous solutions is characterized by its alkaline nature and its ability to influence the concentrations of carbonate and bicarbonate ions, which in turn drive several crucial water treatment processes.
When soda ash is introduced into water, it readily dissociates into its constituent ions: sodium cations (Na+) and carbonate anions (CO32−). This initial dissociation can be represented by the following chemical equation:
Na2CO3(s)→2Na+(aq)+CO32−(aq)
The carbonate ion (CO32−) is the primary reactive species responsible for the majority of soda ash’s impact on water chemistry. Being a weak base, the carbonate ion readily undergoes hydrolysis, reacting with water molecules to form bicarbonate ions (HCO3−) and hydroxide ions (OH−):
CO32−(aq)+H2O(l)⇌HCO3−(aq)+OH−(aq)
The production of hydroxide ions (OH−) is the reason why solutions of soda ash are alkaline, meaning they have a pH greater than 7. This increase in hydroxide ion concentration is the fundamental mechanism by which soda ash raises the pH of water, a crucial step in neutralizing acidic waters and optimizing various other treatment processes. The bicarbonate ion (HCO3−) formed in this hydrolysis reaction also plays a vital role as a buffer in the water, resisting significant changes in pH upon the addition of acids or bases. This buffering capacity provided by the carbonate-bicarbonate equilibrium, established through the dissolution of soda ash, is essential for maintaining a stable pH during water treatment processes.
One of the most significant applications of soda ash’s alkaline nature is in pH adjustment and alkalinity control. Many water treatment processes, such as coagulation, disinfection, and corrosion control, are highly pH-dependent. Acidic raw water can corrode pipes and infrastructure, as mentioned earlier. The addition of soda ash effectively neutralizes this acidity by reacting with hydrogen ions (H+) present in the water, shifting the equilibrium of the carbonate-bicarbonate system and consuming the excess acidity:
CO32−(aq)+2H+(aq)→H2CO3(aq)⇌H2O(l)+CO2(g)
HCO3−(aq)+H+(aq)→H2CO3(aq)⇌H2O(l)+CO2(g)
By consuming these hydrogen ions, soda ash effectively raises the pH to a desired range, typically slightly alkaline, which is optimal for many treatment processes and for preventing corrosion in distribution systems. Furthermore, the carbonate and bicarbonate ions introduced by soda ash contribute to the water’s alkalinity, which is a measure of its capacity to neutralize acids. Maintaining adequate alkalinity is crucial for buffering against pH fluctuations throughout the treatment and distribution systems.
Beyond pH adjustment, soda ash plays a critical role in water softening through a process called precipitative softening. Hardness in water is primarily caused by dissolved calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions. The carbonate ions (CO32−) introduced by the dissolution of soda ash react with these divalent cations to form insoluble precipitates of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and magnesium carbonate (MgCO3):
Ca2+(aq)+CO32−(aq)→CaCO3(s)
Mg2+(aq)+CO32−(aq)→MgCO3(s)
These solid precipitates can then be physically removed from the water through sedimentation and filtration. This process effectively reduces the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions, thereby softening the water and mitigating the problems associated with hardness, such as scale formation and reduced soap effectiveness. While lime (calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2) is also commonly used for water softening, soda ash is often used in conjunction with lime, particularly for removing non-carbonate hardness (hardness associated with anions other than carbonate).
Furthermore, the increase in pH caused by the addition of soda ash can indirectly aid in the removal of certain dissolved metals. Many metal ions, such as iron (Fe2+ and Fe3+) and manganese (Mn2+), become significantly less soluble at higher pH values. At alkaline pH, these metal ions react with hydroxide ions (OH−) to form insoluble metal hydroxides that precipitate out of the water:
Fe2+(aq)+2OH−(aq)→Fe(OH)2(s)
Fe3+(aq)+3OH−(aq)→Fe(OH)3(s)
Mn2+(aq)+2OH−(aq)→Mn(OH)2(s)
The elevated pH provided by soda ash shifts these equilibrium reactions towards the formation of solid metal hydroxides, which can then be removed through sedimentation and filtration. This indirect role in metal removal highlights the importance of pH control in overall water treatment efficiency.
In the context of coagulation and flocculation, the pH adjustment achieved by soda ash is often crucial for optimizing the performance of chemical coagulants. Coagulants, such as aluminum sulfate (alum, Al2(SO4)3) and ferric chloride (FeCl3), work by neutralizing the surface charges of suspended particles, allowing them to aggregate into larger flocs. The effectiveness of these coagulants is highly dependent on the pH of the water. Soda ash can be used to adjust the pH to the optimal range for the specific coagulant being used, ensuring efficient floc formation and subsequent removal of suspended solids and associated contaminants. For example, the hydrolysis of alum is most effective within a specific pH range, and soda ash can be used to maintain this optimal pH.
In summary, the chemistry of soda ash in water is characterized by its dissolution into sodium and carbonate ions, the subsequent hydrolysis of carbonate ions to form bicarbonate and hydroxide ions, and the resulting increase in pH and alkalinity. These chemical transformations underpin its diverse applications in water treatment, including pH adjustment, water softening through precipitation of calcium and magnesium carbonates, indirect aid in the removal of certain dissolved metals by promoting the formation of insoluble hydroxides, and optimization of coagulation and flocculation processes through pH control. Understanding these fundamental chemical reactions is essential for effectively utilizing the power of soda ash in producing clean and safe water.
Key Applications of Soda Ash in Water Treatment
The unique chemical properties of soda ash, particularly its alkalinity and ability to precipitate hardness-causing ions, translate into a wide range of critical applications across the spectrum of water treatment. From ensuring the potability of drinking water in municipal plants to managing the complex effluents of industrial facilities and maintaining the quality of recreational water bodies, soda ash serves as a versatile and often indispensable tool. Its effectiveness in addressing fundamental water quality challenges makes it a cornerstone of modern water treatment practices.
One of the most widespread applications of soda ash is in pH adjustment and alkalinity control. As discussed previously, maintaining the correct pH is paramount in various stages of water treatment and throughout the water distribution system. Raw water sources often exhibit fluctuations in pH due to natural processes or contamination. Acidic water, with a pH below 7, can corrode pipes made of metal (like lead and copper), leading to the leaching of harmful substances into the drinking water. Municipal water treatment plants routinely utilize soda ash to raise the pH of raw water to a slightly alkaline range (typically between 7.5 and 8.5). This neutralization not only protects the infrastructure from corrosion but also optimizes the effectiveness of other treatment processes, such as disinfection with chlorine, which works best within a specific pH range. Furthermore, the addition of soda ash increases the water’s alkalinity, its capacity to buffer against sudden pH changes. This buffering capacity is crucial for maintaining a stable pH throughout the distribution network, preventing fluctuations that could compromise water quality or damage pipes.
Beyond municipal drinking water treatment, soda ash plays a vital role in industrial wastewater treatment. Industrial processes often generate wastewater with extreme pH values, either highly acidic or highly alkaline, and containing a variety of contaminants, including heavy metals and other industrial chemicals. Before this wastewater can be safely discharged into the environment or reused, it requires thorough treatment. Soda ash is frequently employed to neutralize acidic industrial effluents, bringing the pH within acceptable discharge limits mandated by environmental regulations. This pH adjustment is often a prerequisite for subsequent treatment steps, such as the precipitation of heavy metals. By raising the pH with soda ash, many dissolved metals form insoluble hydroxides or carbonates that can then be separated from the wastewater through sedimentation and filtration. This application is crucial in minimizing the environmental impact of industrial activities and ensuring the protection of receiving water bodies.
The application of soda ash extends to the treatment of water in swimming pools and recreational water bodies. Maintaining the proper pH balance in these systems is essential for bather comfort, the effectiveness of disinfectants like chlorine, and the prevention of algae growth. Low pH can cause irritation to the eyes and skin of swimmers and can also corrode pool equipment. Soda ash is commonly used to raise the pH of pool water to the ideal range (typically 7.2 to 7.8), ensuring swimmer comfort and optimizing the sanitizing power of chlorine. Additionally, maintaining adequate alkalinity, achieved with the help of soda ash, stabilizes the pH and prevents wild fluctuations that can be difficult to manage.
Another significant application of soda ash is in water softening. In regions where the raw water supply is hard due to high concentrations of dissolved calcium and magnesium ions, water softening is a crucial treatment step. Municipal water treatment plants often employ precipitative softening processes, where chemicals like lime (calcium hydroxide) and soda ash are added to precipitate calcium and magnesium carbonates. While lime primarily removes carbonate hardness (hardness associated with bicarbonate ions), soda ash is particularly effective in removing non-carbonate hardness (hardness associated with other anions like sulfates and chlorides). The addition of soda ash provides the necessary carbonate ions to react with the remaining calcium and magnesium ions after lime treatment, ensuring a more complete softening process. The resulting calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate precipitates are then removed through sedimentation and filtration. While home water softeners typically utilize ion exchange resins, soda ash plays a critical role in large-scale municipal softening processes.
Furthermore, soda ash contributes to corrosion control in water distribution systems. As mentioned earlier, maintaining a slightly alkaline pH, achieved through the addition of soda ash, helps to form a protective layer inside pipes, preventing the leaching of metals like lead and copper from the pipe material into the drinking water. This is particularly important in older infrastructure where lead pipes or lead-based solder may be present. By ensuring a stable and slightly alkaline pH, soda ash plays a vital role in delivering safe and lead-free drinking water to consumers.
The influence of soda ash also extends to coagulation and flocculation, critical processes for removing suspended solids and turbidity from water. While soda ash is not a coagulant itself, its ability to adjust the pH to an optimal range is often essential for the effective performance of chemical coagulants like aluminum sulfate (alum) and ferric chloride. These coagulants work by neutralizing the surface charges of suspended particles, allowing them to clump together into larger, heavier flocs that can be easily settled or filtered out. The hydrolysis reactions of these coagulants are highly pH-dependent, and soda ash is used to buffer the water within the ideal pH range for efficient floc formation. Without proper pH adjustment using soda ash, the coagulants may not function effectively, leading to poor removal of turbidity and other particulate matter.
In some specific applications, soda ash can also indirectly contribute to algae control. While not an algicide, maintaining a proper pH balance through the use of soda ash can help create an environment less conducive to excessive algal growth in certain water systems, particularly recreational waters. By ensuring stable water chemistry, soda ash can contribute to overall water quality management and reduce the likelihood of nuisance algal blooms.
In conclusion, the applications of soda ash in water treatment are diverse and far-reaching. Its fundamental ability to adjust pH and provide carbonate ions makes it an indispensable chemical in municipal drinking water treatment for pH control, alkalinity enhancement, water softening, and corrosion inhibition. Its role in industrial wastewater treatment for neutralization and metal precipitation is crucial for environmental protection. Furthermore, its use in recreational water bodies ensures bather comfort and effective disinfection. Finally, its indirect contribution to coagulation, flocculation, and potentially algae control underscores its versatility as a key player in the complex science of water treatment. The effectiveness and relatively low cost of soda ash ensure its continued importance in providing clean and safe water for a wide range of needs.
Advantages of Using Soda Ash in Water Treatment
The widespread adoption of soda ash in water treatment is not accidental. Its continued prominence stems from a compelling array of advantages that make it a preferred chemical for addressing numerous water quality challenges. From economic considerations and operational efficiency to environmental factors and its inherent effectiveness, soda ash offers a robust and often superior solution compared to alternative treatment chemicals. Understanding these benefits underscores why it remains a cornerstone of sustainable water management practices globally.
One of the most significant advantages of using soda ash in water treatment is its cost-effectiveness. Compared to many other specialized chemicals used for pH adjustment, softening, or metal precipitation, soda ash is generally a relatively inexpensive commodity chemical. Its widespread availability and well-established production processes contribute to its competitive pricing. This economic advantage is particularly crucial for large-scale municipal water treatment plants and industrial facilities that require significant quantities of treatment chemicals on a continuous basis. The lower cost of soda ash translates to reduced operational expenses, making clean water production and wastewater treatment more economically sustainable in the long run, ultimately benefiting both consumers and industries.
Furthermore, soda ash boasts high availability and ease of handling. It is produced in large quantities globally, ensuring a reliable and consistent supply chain. Its solid, granular form makes it relatively easy to store, transport, and handle compared to some liquid or highly reactive chemicals. While proper safety precautions are always necessary when handling any chemical, soda ash is generally considered less hazardous and easier to manage than strong acids or bases. Its stability under normal storage conditions minimizes the risk of spills or degradation, contributing to safer and more efficient operational practices at water treatment facilities. The ease of handling also simplifies the dosing and application processes, often requiring less specialized equipment and training compared to more complex chemicals.
The effectiveness of soda ash in raising pH and alkalinity is another key advantage. Its rapid dissolution in water and the subsequent generation of hydroxide and carbonate ions provide a reliable and efficient means of neutralizing acidic waters. The predictable and controllable increase in pH allows treatment plant operators to fine-tune the water chemistry to optimal levels for various treatment processes. Moreover, the contribution of carbonate and bicarbonate ions to the water’s alkalinity provides crucial buffering capacity, stabilizing the pH and preventing corrosive conditions throughout the distribution system. This dual action of pH adjustment and alkalinity enhancement makes soda ash a highly valuable tool in ensuring both the safety and the treatability of water.
Soda ash offers dual benefits in addressing multiple water quality issues simultaneously. For instance, in water softening applications, the addition of soda ash not only precipitates calcium and magnesium ions, reducing hardness, but also raises the pH, which can be beneficial for subsequent treatment stages or for corrosion control. Similarly, when used to enhance the precipitation of heavy metals by raising the pH, soda ash also contributes to alkalinity, providing a more stable water matrix for downstream processes. This ability to tackle multiple problems with a single chemical input streamlines the treatment process, reduces the need for multiple chemical additions, and can lead to overall operational efficiencies.
From an environmental perspective, soda ash is generally considered a relatively benign chemical when used correctly. Its primary components, sodium and carbonate, are naturally occurring. While excessive discharge of highly alkaline water can impact aquatic ecosystems, the controlled use of soda ash within treatment facilities, followed by appropriate neutralization if necessary, minimizes its environmental footprint. Compared to some synthetic organic chemicals or highly reactive inorganic compounds used in water treatment, soda ash poses a lower risk of persistent environmental contamination or the formation of harmful byproducts. Its natural origin and relatively simple chemistry contribute to its more favorable environmental profile.
Furthermore, soda ash can enhance the effectiveness of other treatment processes. Its role in optimizing the pH for coagulation and flocculation, as well as for disinfection with chlorine, has already been discussed. By creating the ideal chemical environment, soda ash ensures that other treatment chemicals work more efficiently, leading to better removal of contaminants and a higher quality of treated water. This synergistic effect amplifies the overall effectiveness of the water treatment plant and can potentially reduce the required dosage of other, potentially more hazardous, chemicals.
In specific applications, such as the treatment of certain industrial wastewaters containing specific metals, soda ash can offer advantages over other alkaline agents like lime (calcium hydroxide). The solubility of the resulting metal carbonates can sometimes be lower than that of metal hydroxides formed with lime, leading to more efficient removal. Additionally, the use of soda ash may produce less sludge volume compared to lime in some softening applications, reducing the costs associated with sludge disposal.
Finally, the long history of soda ash use in water treatment provides a wealth of knowledge and established best practices for its application. Treatment plant operators are familiar with its properties, handling requirements, and optimal dosage ranges for various scenarios. This extensive experience translates to more predictable and reliable treatment outcomes. The well-understood chemistry of soda ash in water allows for accurate calculations and effective process control.
In conclusion, the advantages of using soda ash in water treatment are numerous and compelling. Its cost-effectiveness, availability, ease of handling, effectiveness in pH and alkalinity control, ability to address multiple water quality issues, relatively benign environmental profile, and its capacity to enhance other treatment processes make it a preferred choice for water treatment professionals worldwide. As the demand for clean and safe water continues to grow, soda ash will undoubtedly remain a vital and advantageous chemical in ensuring sustainable and effective water management for communities and industries alike.
Considerations and Best Practices for Using Soda Ash
While soda ash offers numerous advantages in water treatment, its effective and safe application necessitates careful consideration of several factors and adherence to best practices. Improper use can lead to unintended consequences, reduced treatment efficiency, and potential safety hazards. Therefore, a thorough understanding of these considerations is crucial for maximizing the benefits of soda ash while minimizing any potential drawbacks.
One of the most critical considerations is dosage control. Determining the appropriate amount of soda ash to add to water is paramount for achieving the desired treatment outcomes without causing over-alkalization. Overdosing soda ash can result in excessively high pH levels, which can be detrimental to aquatic life if discharged into the environment, and can also interfere with certain treatment processes. For instance, excessively high pH can reduce the effectiveness of some disinfectants and may lead to the precipitation of other dissolved minerals that were not intended for removal. Accurate dosage calculation requires careful analysis of the raw water chemistry, including its initial pH, alkalinity, hardness, and the specific treatment goals. Regular monitoring and adjustment of the soda ash dosage based on real-time water quality data are essential for maintaining optimal treatment efficiency and preventing adverse effects. This often involves sophisticated dosing systems and trained personnel who understand the chemical reactions involved and can interpret water quality parameters effectively.
Closely linked to dosage control is the need for water chemistry monitoring. Regular and comprehensive analysis of the water at various stages of the treatment process is crucial when using soda ash. This includes monitoring pH, alkalinity, hardness, and the concentration of other relevant ions. Tracking these parameters allows operators to assess the effectiveness of the soda ash addition, make necessary adjustments to the dosage, and identify any potential imbalances or unintended reactions. Modern water treatment plants often employ online monitoring systems and laboratory analyses to ensure continuous and accurate water quality data, enabling proactive management of the soda ash application. Without diligent monitoring, it becomes difficult to optimize the treatment process and ensure the consistent production of high-quality water.
Handling and safety precautions are also of utmost importance when working with soda ash. While generally considered less hazardous than strong acids or bases, soda ash is still a chemical that can cause irritation upon contact with skin, eyes, and the respiratory system. Inhalation of soda ash dust can lead to coughing and sneezing, while direct contact with skin can cause dryness and irritation. Eye contact can result in more severe irritation and potential corneal damage. Therefore, personnel handling soda ash must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, gloves, and dust respirators, especially during the handling of powdered or granular forms. Proper storage of soda ash in a dry, well-ventilated area is also essential to prevent caking and ensure its quality over time. Emergency procedures for spills and accidental exposure should be in place and readily accessible to all personnel. Training on the safe handling and storage of soda ash is a fundamental requirement for all water treatment plant staff.
Another important consideration is the potential for scaling. While soda ash is used to prevent scaling caused by hard water, excessive addition in softening processes can sometimes lead to the precipitation of calcium carbonate in undesirable locations, such as within pipes or treatment equipment, if not managed correctly. This is particularly relevant in systems with high initial hardness levels. Careful control of the precipitation process, often involving multi-stage treatment or the use of other chemicals in conjunction with soda ash, is necessary to ensure that scaling occurs in designated areas (like clarifiers) where the precipitates can be easily removed, rather than within the distribution system or treatment infrastructure. Monitoring for scale formation and implementing preventative measures, such as maintaining appropriate flow rates and periodically cleaning equipment, are essential best practices.
The compatibility of soda ash with other treatment processes must also be carefully evaluated. Soda ash can interact with other chemicals used in water treatment, and these interactions can either be beneficial or detrimental. For example, the pH adjustment provided by soda ash can significantly impact the effectiveness of coagulants and disinfectants. Understanding these interactions is crucial for optimizing the overall treatment train. Introducing soda ash at the wrong stage or in combination with incompatible chemicals can reduce treatment efficiency or even lead to the formation of undesirable byproducts. Thorough knowledge of the chemical reactions involved in the entire water treatment process is necessary to ensure that soda ash is integrated effectively and safely. Pilot studies and jar tests are often conducted to determine the optimal sequence and dosage of different treatment chemicals, including soda ash, for specific water sources.
Finally, the quality of the soda ash itself can be a factor to consider. Different grades of soda ash are available, with varying levels of purity and particle size. The choice of grade may depend on the specific application and the requirements of the treatment process. Using high-quality soda ash ensures consistent and predictable results and minimizes the introduction of unwanted impurities into the water. Establishing clear purchasing specifications and quality control measures for soda ash supplies is a prudent best practice for water treatment facilities.
In conclusion, while soda ash offers significant advantages in water treatment, its effective and safe use requires careful attention to dosage control, thorough water chemistry monitoring, strict adherence to handling and safety precautions, awareness of the potential for scaling, consideration of its compatibility with other treatment processes, and ensuring the use of appropriate quality soda ash. By implementing these considerations and following best practices, water treatment professionals can maximize the benefits of soda ash in producing clean, safe, and sustainable water supplies while minimizing potential risks to human health and the environment. Continuous learning, adaptation based on monitoring data, and adherence to established safety protocols are essential for the responsible and effective application of this valuable chemical in the crucial field of water treatment.
Question is how Soda Ash is made?
Soda ash can be produced through two main methods: natural extraction and synthetic production.
Natural Soda Ash Production
Natural soda ash is extracted from trona ore, a naturally occurring mineral. Trona ore is a non-marine evaporite mineral that consists primarily of sodium sesquicarbonate (Na2CO3·NaHCO3·2H2O). It is found in large deposits in a few locations around the world, such as:
- Green River Basin, Wyoming (USA): Home to the largest known trona deposits.
- Turkey: Significant trona reserves in the Ankara region.
- Kenya: Home to the Lake Magadi deposit, one of the largest natural soda ash sources in the world.
What is Trona Ore?
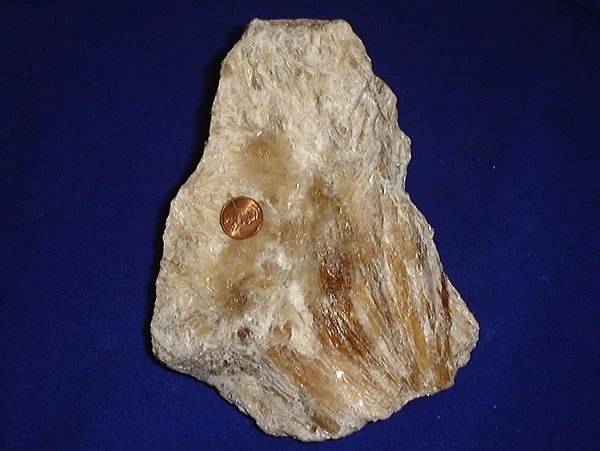

Trona ore is a naturally occurring mineral that primarily consists of sodium sesquicarbonate (Na2CO3·NaHCO3·2H2O). It is formed through the evaporation of alkaline lakes over thousands of years. Trona is the primary source of natural soda ash and is valued for its high sodium carbonate content.
Key Properties of Trona Ore:
- Chemical Composition: Sodium sesquicarbonate.
- Appearance: White or grayish mineral.
- Uses: Primarily used for soda ash production, but also in some niche applications like air pollution control.
Process of Natural Extraction:
- Mining: Trona ore is mined from underground deposits using conventional mining techniques.
- Crushing and Heating: The mined trona ore is crushed and heated to decompose it into soda ash (sodium carbonate), water, and carbon dioxide.
- Purification: The resulting soda ash is purified to remove impurities, producing a high-quality product ready for industrial use.
Natural soda ash production is considered more environmentally friendly than synthetic methods because it requires less energy and generates fewer byproducts.
Synthetic Soda Ash Production
In regions where natural trona deposits are not available, soda ash is produced synthetically using the Solvay process. This method was developed in the 19th century by Belgian chemist Ernest Solvay and remains the most widely used synthetic production method today.
What is the Solvay Process?
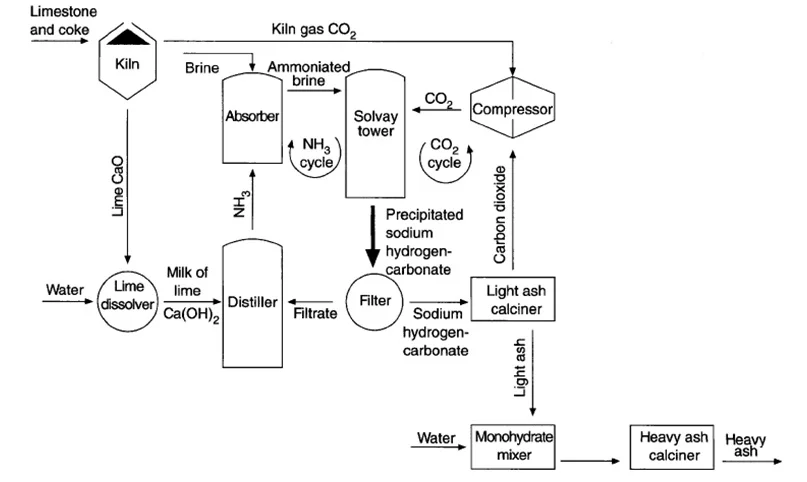
The Solvay process is a chemical reaction that converts salt (sodium chloride) and limestone (calcium carbonate) into soda ash (sodium carbonate) using ammonia as a catalyst. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- Ammoniation of Brine: Saltwater (brine) is mixed with ammonia to form ammoniated brine.
- Carbonation: Carbon dioxide (CO2) is bubbled through the ammoniated brine, producing sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl).
- Filtration: The sodium bicarbonate is filtered out of the solution.
- Calcination: The sodium bicarbonate is heated to produce soda ash (sodium carbonate), water, and carbon dioxide.
- Recovery of Ammonia: The ammonium chloride is treated with lime (calcium oxide) to recover ammonia, which is reused in the process.
Key Features of the Solvay Process:
- Raw Materials: Salt, limestone, and ammonia.
- Byproducts: Calcium chloride (CaCl2), which is often used for de-icing roads or as a drying agent.
- Energy Consumption: The Solvay process is energy-intensive, making it less environmentally friendly compared to natural extraction.
Comparison of Natural and Synthetic Production
| Aspect | Natural Extraction | Synthetic Production (Solvay Process) |
| Raw Materials | Trona ore | Salt, limestone, ammonia |
| Energy Consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Environmental Impact | Less waste and emissions | Generates byproducts like calcium chloride |
| Cost | Lower in regions with trona deposits | Higher due to energy and raw material costs |
| Geographic Availability | Limited to trona-rich regions (e.g., USA, Turkey, Kenya) | Can be implemented anywhere with access to raw materials |
Key Applications of Soda Ash Worldwide
Soda ash is a versatile chemical with a wide range of applications. Here are some of the most common uses:
a. Glass Manufacturing
Soda ash is a key ingredient in glass production, where it acts as a flux to lower the melting point of silica. This reduces energy consumption and makes the glass-making process more efficient. Approximately 50% of global soda ash production is used in the glass industry.
b. Detergents and Cleaning Products
In detergents, soda ash helps soften water by removing calcium and magnesium ions. It also enhances the cleaning efficiency of soaps and detergents.
c. Water Treatment
Soda ash is widely used as a water treatment to adjust pH levels and remove hardness. It is particularly effective in:
- pH adjustment: Increasing the pH of acidic water.
- Water softening: Removing calcium and magnesium ions.
- Pool water treatment: Maintaining optimal pH levels in swimming pools.
d. Chemical Manufacturing
Soda ash is used as a raw material in the production of various chemicals, including sodium silicate, sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), and sodium phosphates.
Uses and Benefits of Soda Ash in Water Treatment
Water treatment Is one of the most important applications of soda ash. Here’s how it works:
a. pH Adjustment
Soda ash is commonly used to increase the pH of acidic water. This is crucial in municipal water treatment plants and industrial processes where low pH can cause corrosion.
b. Water Softening
By reacting with calcium and magnesium ions, soda ash helps remove water hardness. This is essential for preventing scale buildup in pipes and appliances.
c. Pool Water Treatment
In swimming pools, soda ash is used to maintain a pH level between 7.2 and 7.8, ensuring a safe and comfortable swimming environment.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
While soda ash is widely used, it’s important to consider its environmental and safety aspects.
a. Environmental Impact
- Natural soda ash production has a lower environmental footprint compared to synthetic methods.
- The Solvay process generates byproducts like calcium chloride, which can impact the environment if not managed properly.
b. Safety
- Soda ash is generally safe to handle but can cause skin and eye irritation in its concentrated form.
- Proper protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be used when handling soda ash.
Also read: Effective of Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC) for Water Treatment
Soda Ash in Wastewater Treatment
Soda ash is used in wastewater treatment plants for:
- Neutralizing acidic effluents before discharge.
- Enhancing coagulation and flocculation for better sedimentation of impurities.
- Precipitating heavy metals such as lead and copper, reducing environmental pollution.
Safety and Handling of Soda Ash in Water Treatment
While soda ash is generally safe, handling precautions should be followed:
- Wear protective gear (gloves, goggles, and masks) to prevent skin and eye irritation.
- Store in a dry, well-ventilated area to avoid moisture absorption.
- Use appropriate dosing equipment for controlled application.
Conclusion
In the intricate and vital field of water treatment, the journey from raw water to a safe and usable resource involves a carefully orchestrated sequence of processes. Throughout this journey, soda ash, or sodium carbonate, emerges as a remarkably versatile and consistently valuable chemical. Its fundamental alkaline properties and its ability to influence the carbonate-bicarbonate equilibrium in water underpin its effectiveness in addressing a wide spectrum of water quality challenges. From the crucial task of pH adjustment and alkalinity control, ensuring the stability and non-corrosiveness of water, to its significant contribution in water softening by precipitating hardness-causing minerals, soda ash plays a pivotal role in safeguarding water infrastructure and enhancing water quality.
Furthermore, the indirect influence of soda ash in facilitating the removal of dissolved metals through pH manipulation and its ability to optimize the performance of coagulants in turbidity removal highlight its synergistic interactions within complex treatment trains. The economic advantages associated with its widespread availability and relatively low cost, coupled with its ease of handling and generally favorable environmental profile when used responsibly, further solidify its position as a preferred chemical in water treatment facilities worldwide.
However, the effective utilization of soda ash necessitates a thorough understanding of its chemical behavior and a commitment to best practices. Precise dosage control, continuous water quality monitoring, strict adherence to safety protocols, and awareness of potential interactions with other treatment processes are crucial for maximizing its benefits and mitigating any potential drawbacks. The long-standing history of soda ash application in water treatment has fostered a wealth of knowledge and established guidelines for its safe and efficient use.
In conclusion, soda ash stands as a cornerstone of modern water treatment. Its multifaceted applications, ranging from fundamental pH and alkalinity management to facilitating more complex contaminant removal processes, underscore its indispensable role in ensuring the delivery of clean and safe water for communities, industries, and the environment. As water resources face increasing pressures and the demand for high-quality water continues to grow, the reliable and effective application of soda ash will undoubtedly remain a critical component of sustainable water management strategies for the foreseeable future. Its enduring value lies in its simple yet powerful chemistry, making it an essential tool in the ongoing pursuit of clean water for all.

