Monohydrate Citric Acid is a hydrated form of citric acid that contains one molecule of water within its crystalline structure. This compound is widely utilized across various industries due to its versatility, ranging from food and beverage to pharmaceuticals and household cleaning products. This article provides an in-depth discussion of Monohydrate Citric Acid, including its production process, applications, and key differences from anhydrous citric acid.
- What is Monohydrate Citric Acid?
- How is Monohydrate Citric Acid Produced?
- Applications of Monohydrate Citric Acid in Various Industries
- Safety and Regulatory Approval
- Differences Between Monohydrate Citric Acid and Anhydrous Citric Acid
- Proper Storage and Handling
- FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Conclusion
What is Monohydrate Citric Acid?
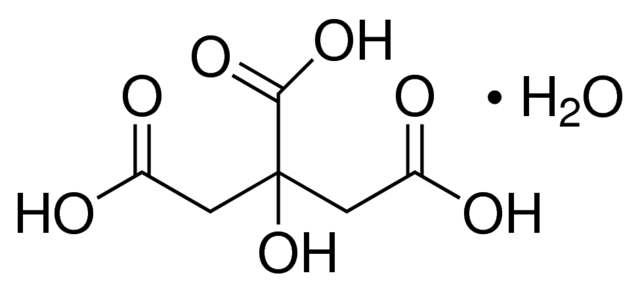
Monohydrate Citric Acid is a form of citric acid that includes one water molecule per crystal unit. This distinguishes it from Anhydrous Citric Acid, which does not contain water. At room temperature, Monohydrate Citric Acid appears as a white crystalline substance with a distinctive sour taste. It is highly soluble in water and commonly used as a natural acidulant and preservative.
Chemical Formula: C₆H₈O₇·H₂O
Type: Organic acid, hydrated form
Molar Mass: 210.14 g/mol
Solubility: Highly soluble in water
How is Monohydrate Citric Acid Produced?
Monohydrate Citric Acid is primarily produced through fermentation. The raw materials, typically glucose or sucrose, undergo fermentation using the microorganism Aspergillus niger. This process yields citric acid, which is then purified and crystallized into its monohydrate form.
Applications of Monohydrate Citric Acid in Various Industries
Due to its multifunctional properties, Monohydrate Citric Acid is widely used across different industries. Some key applications include:
- Food & Beverage Industry: Functions as a pH regulator, natural preservative, and flavor enhancer in carbonated drinks, candies, and processed foods.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in effervescent tablets, buffer solutions, and as an excipient in drug formulations.
- Cosmetics & Skincare: Acts as a pH adjuster and mild exfoliating agent in skincare products like toners and peeling gels.
- Chemical & Cleaning Industry: Found in household cleaning products, such as descalers for removing limescale deposits.
Safety and Regulatory Approval
The use of Monohydrate Citric Acid is approved by various regulatory agencies, including the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States and the EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) in Europe. When used within recommended limits, it is considered safe for consumption. However, excessive intake may lead to gastric irritation or dental erosion due to its acidic nature.
Differences Between Monohydrate Citric Acid and Anhydrous Citric Acid
A primary distinction between Monohydrate Citric Acid and Anhydrous Citric Acid is their water content. Monohydrate contains one water molecule per crystal unit, while anhydrous citric acid is completely devoid of water. This difference affects their stability and usage anhydrous citric acid is preferred for applications requiring moisture-free stability, whereas monohydrate citric acid is more common in liquid formulations.
| Comparison Factor | Monohydrate Citric Acid | Anhydrous Citric Acid |
| Water Content | Contains one water molecule per crystal unit | No water content |
| Physical Form | White crystals | White crystals or powder |
| Stability | More stable in liquid formulations | More stable in dry conditions |
| Common Applications | Frequently used in liquid-based products | Preferred for moisture-sensitive formulations |
| Production Process | Crystallized with water | Produced via dehydration |
Proper Storage and Handling
To maintain its quality, Monohydrate Citric Acid should be stored in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry place. Proper storage prevents moisture absorption, which can lead to clumping and reduced effectiveness.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Conclusion
Monohydrate Citric Acid is a highly versatile chemical compound with applications spanning food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and cleaning chemical industries. Understanding its distinctions from anhydrous citric acid and proper storage methods ensures optimal use across various applications. If you require high-quality Monohydrate Citric Acid for industrial purposes, it is crucial to source it from reputable suppliers.

